Crypto asset liquidity is fragmented across centralised exchanges like Binance, which leads BTC and ETH trading, and decentralised platforms like Uniswap, dominant for DAI. Key metrics show tighter bid-ask spreads on Binance than some stocks, deeper liquidity in crypto-to-crypto pairs, and minimal slippage in stablecoins. External events disrupt liquidity, while ETFs boost volumes without surpassing spot trading. Regulatory support and institutional involvement remain vital.

The landscape of cryptocurrency trading is complex and continuously evolving, marked by a fragmented liquidity environment and distinct market mechanisms between centralised and decentralised exchanges. A recent comprehensive study covering data from January 2023 to February 2025 examines the liquidity dynamics of key crypto assets, including Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and prominent stablecoins such as USDC, USDT, and DAI. The analysis focuses on four principal liquidity metrics: trading volume, bid-ask spreads, market depth, and slippage.
Cristina Polizu, Quant Analytics Managing Director, S&P Global Ratings says, “While [crypto] liquidity has been improving over the years with the development of more robust platforms, financial instruments (such as ETFs), and the entry of institutional investors, challenges still exist. Supportive regulatory frameworks and institutional involvement could create a more robust and efficient crypto ecosystem.”
Liquidity within crypto markets remains highly fragmented across various trading venues. Centralised exchanges (CEXs) like Binance maintain dominance in trading volume for major cryptocurrencies such as BTC and ETH. Conversely, decentralised exchanges (DEXs), particularly Uniswap, lead in trading volumes for certain stablecoins, notably DAI. This division illustrates the coexistence of traditional exchange models alongside emerging on-chain trading frameworks.
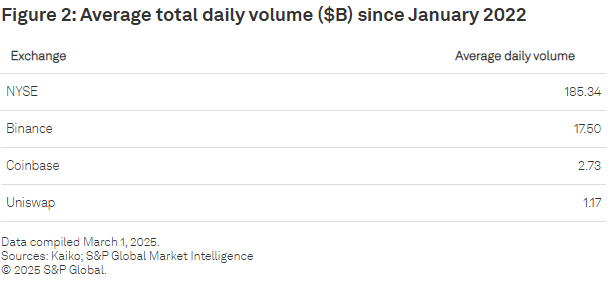
Understanding bid-ask spreads in crypto markets
Bid-ask spreads serve as a critical indicator of liquidity and trading efficiency. The study reveals that digital assets traded on Binance exhibit tighter spreads compared to some S&P 500 stocks, such as Broadcom, although these spreads remain wider than those of highly liquid equities like Apple. Interestingly, BTC and ETH display a strong correlation in their spread patterns, while stablecoins and traditional stocks do not share this relationship. This suggests differing market behaviours and liquidity dynamics between cryptocurrencies and fiat-based assets.
Market depth, which reflects the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels, varies significantly across crypto trading pairs. Crypto-to-crypto pairs, such as BTC-USDT, possess substantially deeper liquidity pools, allowing for larger trades with minimal price impact. In contrast, fiat-to-crypto pairs, for example EUR-USDC, exhibit notably shallower market depth. This shallowness poses challenges for executing large orders without significant price movement, potentially limiting market efficiency in these pairs.
Slippage as an indicator of liquidity conditions
Slippage, the difference between expected and executed trade prices, fluctuates depending on the asset and prevailing market conditions. The report identifies that during periods of heightened volatility, ETH trades may experience slippage rates as high as 4.96%. Conversely, stablecoin pairs such as USDC-DAI demonstrate minimal slippage, underscoring their high liquidity and stable peg relationship. These findings highlight the varying degrees of market resilience across different crypto assets.
The study emphasises the sensitivity of crypto liquidity to external disruptions. Political crises, exemplified by events in South Korea, and security breaches like the Bybit cyberattack, have led to abrupt liquidity contractions and notable price dislocations. These incidents underscore the vulnerability of crypto markets to geopolitical and technological risks, impacting overall market stability.
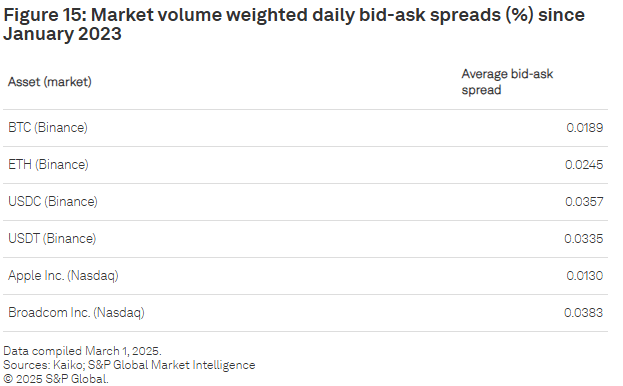
Contrasting mechanisms: Centralised vs. decentralised exchanges
Centralised exchanges operate with traditional order books and custodianship models, closely resembling established financial markets. In contrast, decentralised exchanges rely on Automated Market Makers (AMMs) which facilitate on-chain trading without intermediaries. While AMMs enhance accessibility and decentralisation, they expose liquidity providers to risks such as impermanent loss, influencing participation and liquidity depth on these platforms.
The introduction of Bitcoin and Ethereum exchange-traded funds (ETFs) has stimulated trading activity and increased market participation. Despite this, spot market trading on crypto exchanges continues to surpass ETF volumes, indicating that ETFs complement rather than replace traditional crypto trading avenues. This trend reflects the gradual integration of crypto assets into mainstream financial markets while preserving core exchange activities.
Himani Verma is a seasoned content writer and SEO expert, with experience in digital media. She has held various senior writing positions at enterprises like CloudTDMS (Synthetic Data Factory), Barrownz Group, and ATZA. Himani has also been Editorial Writer at Hindustan Time, a leading Indian English language news platform. She excels in content creation, proofreading, and editing, ensuring that every piece is polished and impactful. Her expertise in crafting SEO-friendly content for multiple verticals of businesses, including technology, healthcare, finance, sports, innovation, and more.








